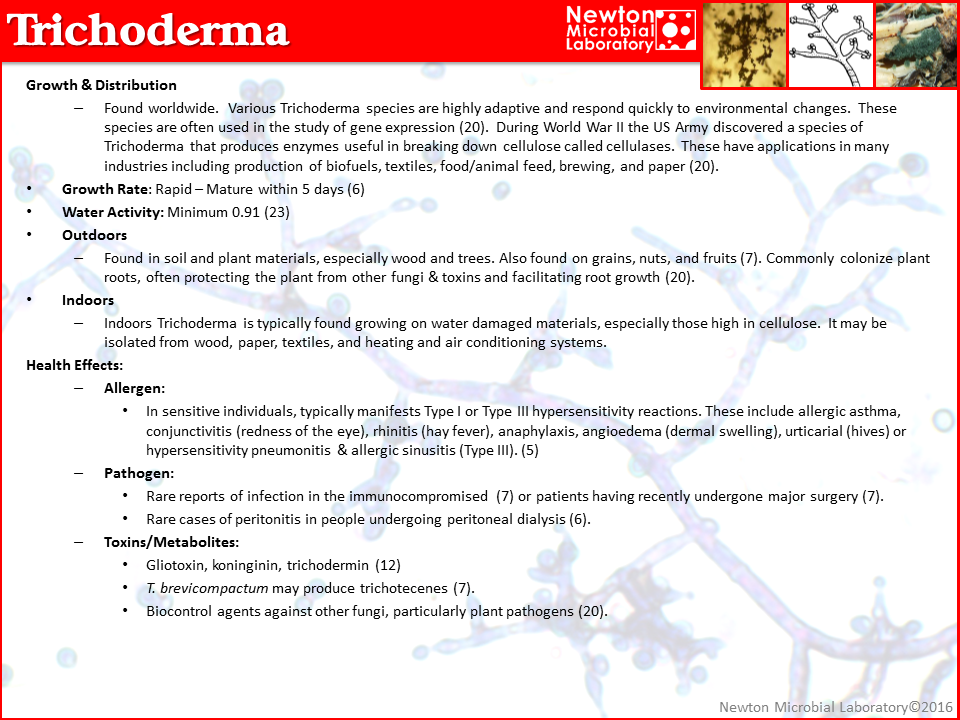
Trichoderma
Growth & Distribution
Found worldwide. Various Trichoderma species are highly adaptive and respond quickly to environmental changes. These species are often used in the study of gene expression (20). During World War II the US Army discovered a species of Trichoderma that produces enzymes useful in breaking down cellulose called cellulases. These have applications in many industries including production of biofuels, textiles, food/animal feed, brewing, and paper (20).
Growth Rate: Rapid – Mature within 5 days (6)
Water Activity: Minimum 0.91 (23)
Outdoors
Found in soil and plant materials, especially wood and trees. Also found on grains, nuts, and fruits (7). Commonly colonize plant roots, often protecting the plant from other fungi & toxins and facilitating root growth (20).
Indoors
Indoors Trichoderma is typically found growing on water damaged materials, especially those high in cellulose. It may be isolated from wood, paper, textiles, and heating and air conditioning systems.
Health Effects
Allergen:
In sensitive individuals, typically manifests Type I or Type III hypersensitivity reactions. These include allergic asthma, conjunctivitis (redness of the eye), rhinitis (hay fever), anaphylaxis, angioedema (dermal swelling), urticarial (hives) or hypersensitivity pneumonitis & allergic sinusitis (Type III). (5)
Pathogen:
Rare reports of infection in the immunocompromised (7) or patients having recently undergone major surgery (7).
Rare cases of peritonitis in people undergoing peritoneal dialysis (6).
Toxins/Metabolites:
Gliotoxin, koninginin, trichodermin (12)
T. brevicompactum may produce trichotecenes (7).
Biocontrol agents against other fungi, particularly plant pathogens (20).